Taking stock of AI's impact
Much is still unclear, but some things, like the changing face of the Internet, Europe lagging behind and increased importance of data is a discernible trend.
The AI Horizon - Mirages and Milestones: There remains a lot of uncertainty and often diametrically opposed opinions about many of the vexing questions around AI. A comprehensive survey involving 2,778 top-tier AI researchers revealed significant differences in predictions about AI's development pace and impact. Aggregating key projections suggest a 50% likelihood that by 2028, AI will autonomously build a payment site, compose a hit song, and fine-tune large language models independently. Notably, the probability of AI surpassing human cognitive capability across all tasks is seen as 10% as soon as 2027, reaching 50% probability by 2047—13 years sooner than previous estimates given just a year ago. Yet, full automation of all human jobs is given a 10% chance by 2037, with a 50% likelihood way into the future in 2116.
Surpassing GPT4 with Context Windows: Efforts to outperform the capabilities of proprietary, centralized models with smaller, open-source alternatives have intensified. Notably, neither open-source nor propriety ones have beaten ChatGPT’s GPT4 on cognitive benchmarks since its release. Everyone expected Google to lead this, but after unexpected false starts, it has made a significant breakthrough with the release of Gemini 1.5. A proprietary, centralized model itself, it stands out as the first to not only match but, in certain benchmarks, surpass the performance of ChatGPTs GPT4. And in the last fortnight, yet another propriety model, Anthropic’s Claude 3, broadly matched GPT4. Gemini 1.5 introduces multi-modal capabilities, processing inputs across text, audio, and video—a trend gaining momentum in generative AI. Perhaps most significantly, it boasts an impressive "context window" capable of handling up to 1 million tokens. This advancement enables the analysis of entire books under 200,000 words or comprehensive code bases in a single query. In comparison, the current iteration of ChatGPT has quadrupled its initial context window size to 32,000 tokens. The drive for longer context windows reflects the weak points of current model architectures. They have nothing akin to the dynamism of human memory. They are pre-trained or primed on new information via fine-tuning, an expensive process that needs expert human intervention and bespoke data. However, models can be given new information via their context window, a form of working memory limited in size due to the computational cost of processing them at scale — until Gemini.
RAG and Beyond: Research into giving AI easily updatable memory matters. Having no dynamic memory limits an AI's ability to act sequentially on a plan or to get to know you or your business. Up to now, one method to address this, besides expensive one-off fine-tuning, is the so-called Retrieval Augmented Generation or RAG. At the heart of RAG lies the principle of leveraging a repository of information (like documents, web pages, or database entries). The relevant documents are retrieved, usually via search functionality, which is then fed to the generative AI's context window. RAG is, therefore, only as good as the retrieval functionality and is also limited by the context window size. Multiple promising research tracks are now looking at new model architectures (e.g. state space models) that could endow models with something like a dynamic memory (aka episodic memory), which would be another major leap forward.
Embodied Intelligence: The prevailing view suggests that human cognition extends beyond the brain, utilizing the entire body and more for thought processes. This concept has implications for artificial intelligence, where models integrated with sensory and motor functions, or 'embodied AI,' are believed to surpass their text-only counterparts. PaLM-E exemplifies this theory as a cutting-edge, embodied generalist model. With 562 billion parameters and training across visual, linguistic, and robotic datasets, it can manage a robotic manipulator in real-time and achieve unprecedented performance on visual question-answering benchmarks. But PaLM-E's embodiment also allows it to excel in language tasks, especially those requiring an understanding of spatial relationships, showcasing a significant leap over traditional, text-only AI models.
Data Drought: Quality data is becoming only more important for training high-performance models. According to a study by Epoch AI, if current trends in data usage and generation persist, we are on track to deplete our reserves of low-quality language data as soon as 2030, exhaust our supply of high-quality language data by 2026, and run out of vision data sometime between 2030 and 2060. Another avenue is the use of AI-generated synthetic data, though the effectiveness of this approach has shown varying results.
Behind Walls - The Changing Face of the Internet: The growing appreciation for data's worth is transforming the open nature of the Internet. Platforms like Twitter and Reddit are now inaccessible without a login, while the New York Times has initiated a copyright lawsuit against OpenAI for training on its data. And while Getty Images is also suing the owners of Stable Diffusion, Shutterstock has done an image data deal with OpenAI. Moreover, as revealed by internal documents, Tumblr, WordPress.com are reportedly planning to monetize user data through agreements with Midjourney and OpenAI. Reddit will let “an unnamed large AI company” access its user-generated content in a deal “worth about $60 million on an annualized basis”. Meanwhile, Apple, very much behind its competitors, reportedly offers publishers large sums to access their data.
Social Media Data Generators: In another twist, illustrating the data generation flywheel (and value) of social media platforms, new analytics data shows that compared to the most popular incumbent apps such as YouTube (which has a 1-month user retention rate of 85%), Instagram, TikTok or WhatsApp (with a DAU/ MAU ratio of 85%), GenAI apps such as ChatGPT (1-month retention 56%; DAU/MAU 14%), Runway or Character.ai suffer from significantly lower median retention and daily active users, meaning they are also generating a lot less data. In May 2023, only 14% of Americans had used the free and far less able GPT3 tier of ChatGPT, according to Pew.
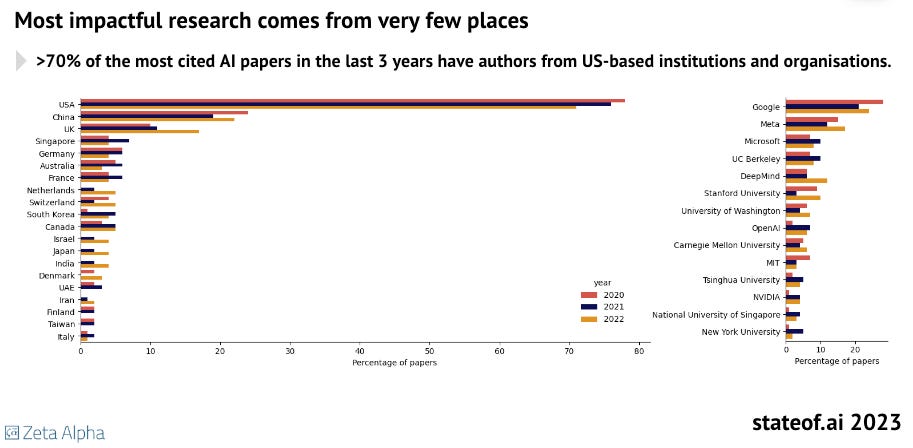
Europe, And Public Funded Research - Not In The AI Race: The most cited research in AI in the last three years has come from very few places, with Europe lagging markedly and the United States dominating the field. It accounts for 70% of all highly cited AI research papers in the past three years, positioning it well ahead of China and the United Kingdom, which rank second and third, respectively. Combined, the contributions from Europe's best performers, Germany and France, match those of the UK. Remarkably, over 40% of the most influential papers originate from just two entities: Google and Meta. Despite this concentration, there's a budding trend where major tech firms (Meta excepted) have begun withholding their research findings, marking a shift in disseminating AI advancements.
Europe's Lack of AI Capital: The revival in the S&P 500 during 2023 can largely be credited to "The Magnificent Seven" - Apple, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Alphabet, Meta, Tesla, and Amazon - which have emerged as major contributors to and beneficiaries of the rapid acceleration in AI technology. Meanwhile, US AI enterprises have attracted 70% of the world’s private AI investment in 2023, marking an increase from 55% the previous year. Investment in European AI ventures has decreased by more than 70% at the same time. Mistral, the leading European start-up and rumoured to be the reason Macron intervened to reduce the regulatory burden of the AI Act, secured a round of funding led by Silicon Valley's Andreessen Horowitz in December 2023, underscoring Europe's capital malaise.
Narrow AI - Wide Impact: Despite receiving less attention, significant progress is continuously being made in specialized or "narrow" AI, particularly the life sciences. Here is just one sample. Creating entirely new proteins with specific desired functionalities or structural characteristics, known as de novo design, is of significant interest to both academic research and the industrial sector. Leveraging their demonstrated success in generating sophisticated models of images and text, diffusion models are now being explored for their potential to revolutionize the field of protein engineering from the ground up.
The AI Paradox - Jobs Amidst Uncertainty: Across the Western world, we are at a time of exceptionally low unemployment. And overall, the most recent research on robot and AI diffusion points to positive productivity gains and an increase in employment at the firms that adopt it. Employment effects at the industry level are less clear-cut. Yet, anecdotes of AI-induced job losses abound. It may simply be too early to observe the aggregate productivity and employment effects of AI.
A Future Unevenly distributed: While acknowledging considerable uncertainty, the IMF predicts that nearly 40% of jobs worldwide will be impacted by AI, with workers in advanced economies facing higher exposure but also standing to gain more on aggregate from AI's benefits compared to those in emerging and developing countries. In advanced nations, around 60% of employment involves cognitive tasks that AI could impact soon, with potential outcomes evenly split between job losses and productivity boosts through AI being integrated with workers' tasks. This would lead to higher wages for those workers and a widening gap between these winners and the losers. Key, however, should be the aggregate higher growth and overall increase in employment in these economies. Emerging markets see a 40% exposure rate, while only 26% of jobs in low-income countries are similarly touched by AI. However, the limited exposure of these economies to AI widens the aggregate digital and economic gaps between wealthy and poor regions. If these productivity levels are achieved along with large-scale job disruption, expect calls on governments to help workers transition to new roles to grow.
The 700-Agent AI: Klarna, the Buy Now Pay Later pioneer, reports remarkable efficiency gains with its OpenAI-powered chatbot, achieving the workload of 700 full-time employees since its worldwide debut last month. This AI assistant has managed 2.3 million conversations, accounting for two-thirds of all customer service interactions. The implementation of the chatbot has resulted in a 25% reduction in follow-up queries, enabling customers to find solutions in under two minutes—a significant improvement from the previous eleven-minute average. A survey by legal publishing firm Lexus Nexus indicates that the majority (80%) of Fortune 1000 executives expect to see a reduction in billing from outside legal counsel due to the ability to bring work in-house because of generative AI (80%).
AI Joins the Culture War: ChatGPT has become a flashpoint in a series of heated cultural debates, largely in the US, with particularly conservatives sharing screenshots to allege bias in ChatGPT’s training and fine-tuning. The heat was turned up several fold when a viral post showed that Gemini's recently launched AI image generator created an image of the US Founding Fathers, which mistakenly included a black man. Elon Musk is working on his own models and Musk emphasised that “our AI can give answers that people may find controversial even though they are actually true”. Meanwhile, Mistral, Europe's leading general purpose AI start-up, has launched a new Mistral Large model that is touted as a multilingual, culturally sensitive alternative to models that have only been trained on English language data. It is natively fluent in English, French, Spanish, German, and Italian, with “a nuanced understanding” of grammar and cultural context. Meanwhile, the Spanish PM has announced a private-public partnership to build an AI model in Spanish and other regional languages.
Chip War Champs - Too Early to Call: Amid tightening restrictions, Huawei surprised the world with its new Mate 60 Pro phone, powered by the advanced Kirin 9000S chip produced by Chinese chipmaker SMIC. Yet the 7-nanometer chip is no longer state of the art, and this advance still leaves SMIC lagging behind Taiwan's TSMC by half a decade. With access to more advanced lithography machines from the Netherlands' ASML cut-off, it may be much harder for China to achieve 5nm. In 2023, all eyes were on NVIDIA’s new H100 GPU, the more powerful successor to the A100, both banned for export to China. While H100 clusters are being built, researchers rely on the V100, A100 and RTX 3090. It is quite remarkable how much competitive longevity NVIDIA products have The State of AI 2023 points out: the V100, released in 2017, is still the most commonly used chip in AI research. This suggests A100s, released in 2020, could peak in 2026 when the V100 is likely to hit its trough. It also suggests we won't know if Biden's chip ban is successful for some time yet. Meanwhile, an analysis by Bloomberg shows that an invasion of Taiwan would have a bigger impact on the global economy than the financial crisis, partly because of the impact on chip availability and resulting Western sanctions impact on trade.
Social Engineering Phishing Spike: Darktrace reports a staggering 135% increase in these phishing attacks among its extensive customer base from January to February 2023. This trend is strongly associated with the swift integration of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT into mainstream technology. In a year that sees multiple elections around the world, the misinformation threat that AI poses is one of the most immediate.
The EU AI Act's Wings Clipped: In December 2023, following last-minute French concerns, a consensus was reached on the EU AI Act to protect European start-ups from burdensome requirements when developing generalist AI models. The legislation distinguishes between general purpose models and those deemed to pose a systemic risk, which is determined either by the computational power used in training—specifically, if it surpasses a benchmark akin to GPT-4's capabilities—or through identification by the Commission. Providers of AI models categorized under systemic risk must now conduct standardized evaluations, address and mitigate potential systemic risks, monitor and report any incidents, and ensure cybersecurity measures.
AI Act Exclusions - Military, Research, Open-Source and Fraud: The AI Act delineates specific exemptions, excluding military AI systems and those solely dedicated to scientific research and development from its purview. Free and open-source AI systems are exempt unless they fall into prohibited or high-risk categories. Notably, AI systems used in credit scoring are classified as high-risk, entailing additional requirements. However, AI systems mandated by Union law for financial fraud detection or for assessing the capital requirements of banks and insurance companies do not fall under the high-risk category. The European Parliament has revised its stance on the outright prohibition of real-time remote biometric identification, opting instead for an approach that allows narrow exceptions for law enforcement, particularly in preventing terrorism or identifying individuals involved in serious crimes. The regulations for post-event usage of this technology will be more lenient too.
Europe's Regulatory Data-Danger: The agreement on the AI Act was hailed as a success. Yet the impact of EU regulations on the development of AI for the benefit of the European economy may lie elsewhere, in regulations that touch on data, like the Data Governance Act, Data Act, DSA and GDPR. The most impactful AI relies not only on data at scale for its training but also on scope, linking diverse datasets together. The GDPR and subsequent European court rulings like the SHREMS cases make linking data sets difficult and fragment data across borders. The Data Governance Act purports to enable data sharing but explicitly prohibits linking datasets without providing incentives for such sharing. This is a major oversight when the value of data is being reassessed upwards.